Developer Guides
1 Basic Terms
1.1 Sampling Rate
The sampling rate refers to the number of times an audio signal is sampled per second, indicating how frequently the audio signal is sampled. The higher the sampling rate, the more detailed the audio data is preserved, and a higher recognition accuracy is expected.
When using our speech recognition services, you can specify the audio sampling rate as a parameter, and the actual sampling rate of the audio transmitted must match this parameter value. Currently, our speech recognition services only support audio with a sampling rate of 16000 Hz or 8000 Hz.
1.2 Sample Size
The sample size, which measures the variation of sound waves, refers to the number of binary bits used by the sound card when capturing and playing digital audio signals. Currently, our speech recognition services only support a sample size of 16 bits.
1.3 Sound Channel
A channel refers to an independent audio signal that is captured or played back at different spatial positions during recording or playback. Therefore, the number of channels is equivalent to the number of sound sources during recording or the corresponding number of speakers during playback. At present, except for the audio file transcription service which supports the transcription of dual-channel (stereo) files, all other speech recognition services only support single-channel (mono) audio files.
1.4 Language
At present, we support Japanese, Japanese-English mixed, English, Chinese, and Chinese-English mixed languages.
1.5 Intermediate and Final Results
For streaming APIs (WebSocket API of short speech recognition and real-time speech recognition), recognition results are returned in real-time as the speech is input. For example, the sentence "天気がいいです。" might produce the following recognition results during the recognition process:
てんき
天気が
天気がいい
天気がいいです。Among these, the first three lines are called "intermediate results," and the last one is called the "final result." For streaming recognition products, you can control whether to return intermediate results by setting the enable_intermediate_result parameter.
1.6 Word Information
Word information refers to the content of word segmentation during the recognition process, including the current word's text content, start time, and end time. When using real-time speech recognition services, you can specify whether to return word information.
| Item | Intermediate Result Word Information | Final Result Word Information |
|---|---|---|
| Control Parameter | enable_intermediate_words | enable_words |
| Includes: Text content, Start Time, End Time | √ | √ |
| Includes: Word Type | √ | |
| Includes: Word Stability Status | √ |
The word stability status field indicates whether the current word may change in the intermediate results: if it is not true, it indicates that this word may change in later intermediate results. Otherwise, it means the word has stabilized and will not change. This field currently supports the following languages: Chinese, Chinese and English mixed. (That is, language codes starting with zh)
1.7 Inverse Text Normalization (ITN)
Inverse Text Normalization (ITN) refers to the process of displaying dates, numbers, and other objects in speech recognition results in a conventional format, as shown in the table below:
| Without ITN | With ITN |
|---|---|
| 二十パーセント | 20% |
| 千二百三十四円 | 1234円 |
| 四月三日 | 4月3日 |
You can specify whether to enable ITN.
2 Practical Features
2.1 Inverse Text Normalization (ITN)
When using the speech recognition services, you can specify whether to enable ITN by configuring the enable_inverse_text_normalization parameter.
2.2 Hot Words
For some specific proper nouns such as personal names, place names, product names, company names, or specialized terms in a particular field, the recognition accuracy may not be high. These proper nouns can be manually added as "hotwords" to significantly improve the recognition accuracy of the words in the hotwords list.
Hotwords Composition:
-
Japanese & Japanese-English Mixed Language: Set in the form of hotword groups, which consists of "writing, pronunciation, category code". For example:
早稲田大学,ワセダダイガク,0.-
The category is a system-set value. When calling, please select according to the actual situation. If the category in the set hotword group is not a system-set value, the hotword group will be filtered out.
-
Category Options:
Code Catagory 0 no class designation 1 proper noun 2 name 3 given name 4 station name 5 place name 6 company name 7 department name 8 job title 9 symbol 10 open parenthesis 11 close parenthesis 12 era name
-
-
Chinese & Chinese-English Mixed & English Language: Set in the form of hotword, which consists of “writing". For example:
汇演.
For adding/deleting hotwords, please see Hotwors API. You can also edit hotwords at User Panel - Hotwords. After adding hotwords, you can configure the hotwords_id parameter to pass the hotwords ID during recognition to make it effective.
In addition, the platform supports real-time hotwords functionality. There is no need to create a hotword ID in advance. You can simply pass the hotwords list hotwords_list parameter in a single connection/request to make it effective for that session only, and it will be deleted after use.
- Up to 100 hotwords/hotword groups can be uploaded at a time for real-time hotwords.
- If both real-time hotwords
hotwords_listand non-real-time hotwordshotwords_idare used simultaneously, the real-time hotwords will take precedence. - If multiple groups of hotwords are uploaded, they should be separated by
|, such as:早稲田大学,ワセダダイガク,固有名詞|新横浜,シンヨコハマ,5.
When using hotwords (real-time or non-real-time), you can specify the weight of hotwords hotwords_weight. The higher the weight, the higher the recognition accuracy of the words in the hotwords list. However, it will also increase the probability of misrecognizing other similar-sounding words, so the weight parameter needs to be balanced.
Hotwords Automatic Extraction
When creating and modifying hotwords databases, the hotwords automatic extraction function can be used to automatically extract keywords such as personal names, place names, and organization names from the specified text content and use them to train hotwords.
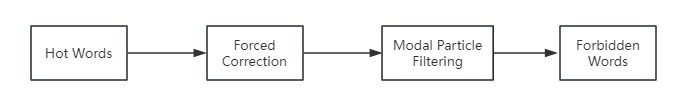
2.3 Forced Correction (Forced Replacement)
For recognition errors that cannot be resolved by hot word optimization, you can manually correct the specified incorrect words by using the forced replacement feature. For example, if the speech recognition service mistakenly recognizes "5G" as "5時", you can manually add a forced replacement rule of "5時→5G" and configure the correction_words_id parameter with the ID during recognition to achieve correct recognition. You can add/delete forced replacement words at User Panel - Customized Word Lists.
2.4 Forbidden Words (Sensitive Words)
For words or phrases that you do not wish to display directly, you can manually add them as "forbidden words." By configuring the forbidden_words_id parameter with the forbidden words' ID during recognition, the forbidden words in the recognition results (including intermediate and final results) will be automatically replaced with a specified character (default is asterisk *). You can refer to User Panel - Customized Word Lists for adding/ deleting forbidden words.
2.5 Filler Word Removal
For common colloquial expressions such as "Oh", "Uh-hum", etc., you can manually add filler word removal rules. By enabling the enable_modal_particle_filter parameter during recognition, the matching filler words can be automatically removed from the recognition results (only the final results). You can refer to User Panel - Customized Word Lists for adding/ deleting filler word removal rules.
Note
The processing priority of the above features is as follows:
2.6 Amplitude Gain
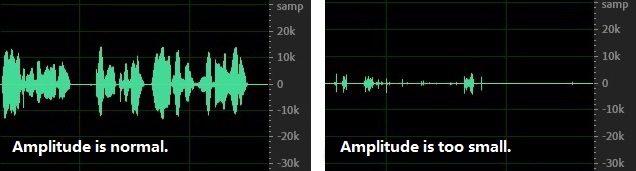
The amplitude of sound determines the volume. Amplitudes that are too high or too low can degrade the accuracy of speech recognition. The recommended amplitude is around 10k, within which the best results for speech recognition can be achieved. As shown in the figure below, the left side has a normal amplitude (range around 10k), while the right side has an insufficient amplitude (range around 1k), thus the recognition effect for the audio on the right side is impaired.
In cases of low amplitude, improvements can be made in two ways. One is by adjusting the recording method, such as the distance between the speaker and the microphone, or the microphone/recording parameter settings, to address the issue of low volume at the original audio level. The other is by using the amplitude gain parameter gain in the speech recognition service to amplify the original audio amplitude before performing speech recognition processing.
2.7 File Upload Methods for Audio File Transcription
For audio file transcription, two upload methods are supported: audio URL and audio file. These two methods cannot be used simultaneously.
2.8 Output Formats for Audio File Transcription
For the audio file transcription service, the output format can be configured by the output parameter.
- Script format: Suitable for long texts such as manuscripts, with normal punctuation based on pauses in speech.
- Subtitle format: Optimized for subtitles, with shorter sentences and no punctuation at the end of sentences.
2.9 Role Differentiation for Audio File Transcription
Role Differentiation can be achieved in two ways: by audio channels or by speaker diarization. The two methods cannot be used simultaneously.
2.10 Automatic Keyword Extraction for Audio File Transcription
When uploading an audio file, you can specify the maximum number of keywords, and the system will automatically extract up to that number of keywords, which can be sorted based on relevance and frequency. This feature only supports Chinese and Chinese-English mixed.
2.11 Speech Speed Calculation for Audio File Transcription
We offer automatic calculation of average speech speed. For Japanese and Chinese, the unit is characters per minute. For English, the unit is words per minute.
3 Audio Encoding
Currently, the speech recognition services support the following audio encoding formats. Please set the format field to the corresponding encoding format.
| Encoding Format | Description | Short Speech Recognition, Real-Time Speech Recognition | Audio File Transcription (Standard) | Audio File Transcription (VIP) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pcm | Uncompressed audio with a sample width of 16 bit, Little-Endian. Common in regular uncompressed WAV formats (excluding the first 44 bytes of WAV header). | √ | √ | √ |
| wav | Audio with a sample width of 16 bit. | √ | √ | √ |
| opus | OPUS format encapsulated in an OGG container, with a framesize of at least 60 ms. | √ | √ | |
| mp3 | √ | √ | √ | |
| mp4 | √ | |||
| m4a | √ | √ | ||
| amr | √ | √ | ||
| 3gp | √ | |||
| aac | √ | √ |
4 Language Support
Language codes follow the format of language-variant-script-region.
- language: The language code (ISO 639-1) in lowercase, such as " ja" for Japanese and "en" for English
- variant (optional): The pronunciation or dialect code (ISO 639-3) in lowercase, for example, "cmn" for Mandarin and "yue" for Cantonese
- script (optional): The script variant code (ISO 15924) with the first letter capitalized, such as "Hans" for Simplified Chinese and "Hant" for Traditional Chinese.
- region: The geographical region code (ISO 3166) in uppercase, such as "JP" for Japan and "CN" for Mainland China .
Currently, the speech recognition services support the following languages. Please set the lang_type (or langType, depending on the SDK used) field to the corresponding language code.
| Language | Language Code | Sampling Rate (Hz) | Short Speech Recognition, Real-Time Speech Recognition | Audio File Transcription(Standard & VIP) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Japanese | ja-JP | 16K | √ | √ |
| 8k | √ | √ | ||
| Japanese-English Mixed | jaen-JP | 16K | √ | √ |
| 8k | √ | √ | ||
| English | en-US | 16K | √ | √ |
| 8k | √ | √ | ||
| Chinese | zh-cmn-Hans-CN | 16K | √ | √ |
| 8k | √ | √ | ||
| Chinese-English Mixed | zhen-cmn-Hans-CN | 16K | √ | √ |
| 8k | √ | √ |